Tutorial
- How To Decrypt Htpasswd Password Reset
- How To Decrypt Htpasswd Password Cmd
- How To Decrypt Htpasswd Passwords
- Decrypt A Password For Free
- Htpasswd Decrypt Password
- How To View Encrypted Password
Short answer: no. Try cheating: at the same time you write the login and encrypted password to your htpassword file, write the login and unencrypted password to a hidden file accesable only to you for future reference. How does htaccess passwd 'encryption' work OR How can I decrypt it? Note: This is for educational purposes only. Premium Content You need an Expert Office.
Introduction
How To Decrypt Htpasswd Password Reset
When setting up a web server, there are often sections of the site that you wish to restrict access to. Web applications often provide their own authentication and authorization methods, but the web server itself can be used to restrict access if these are inadequate or unavailable.
In this guide, we’ll demonstrate how to password protect assets on an Apache web server running on Ubuntu 14.04.
Prerequisites
To get started, you will need access to an Ubuntu 14.04 server environment. You will need a non-root user with sudo privileges in order to perform administrative tasks. To learn how to create such a user, follow our Ubuntu 14.04 initial server setup guide.
Install the Apache Utilities Package
In order to create the file that will store the passwords needed to access our restricted content, we will use a utility called htpasswd. This is found in the apache2-utils package within the Ubuntu repositories.
Update the local package cache and install the package by typing this command. We will take this opportunity to also grab the Apache2 server in case it is not yet installed on the server:
Create the Password File
We now have access to the htpasswd command. We can use this to create a password file that Apache can use to authenticate users. We will create a hidden file for this purpose called .htpasswd within our /etc/apache2 configuration directory.
The first time we use this utility, we need to add the -c option to create the specified file. We specify a username (sammy in this example) at the end of the command to create a new entry within the file:
You will be asked to supply and confirm a password for the user.
Leave out the -c argument for any additional users you wish to add:
If we view the contents of the file, we can see the username and the encrypted password for each record:
Configure Apache Password Authentication
Now that we have a file with our users and passwords in a format that Apache can read, we need to configure Apache to check this file before serving our protected content. We can do this in two different ways.
The first option is to edit the Apache configuration and add our password protection to the virtual host file. This will generally give better performance because it avoids the expense of reading distributed configuration files. If you have this option, this method is recommended.
If you do not have the ability to modify the virtual host file (or if you are already using .htaccess files for other purposes), you can restrict access using an.htaccessfile. Apache uses.htaccess` files in order to allow certain configuration items to be set within a file in a content directory. The disadvantage is that Apache has to re-read these files on every request that involves the directory, which can impact performance.
Choose the option that best suits your needs below.
Configuring Access Control within the Virtual Host Definition
Begin by opening up the virtual host file that you wish to add a restriction to. For our example, we’ll be using the 000-default.conf file that holds the default virtual host installed through Ubuntu’s apache package:
Inside, with the comments stripped, the file should look similar to this:
Authentication is done on a per-directory basis. To set up authentication, you will need to target the directory you wish to restrict with a <Directory ___> block. In our example, we’ll restrict the entire document root, but you can modify this listing to only target a specific directory within the web space:
Within this directory block, specify that we wish to set up Basic authentication. For the AuthName, choose a realm name that will be displayed to the user when prompting for credentials. Use the AuthUserFile directive to point Apache to the password file we created. Finally, we will require a valid-user to access this resource, which means anyone who can verify their identity with a password will be allowed in:
Save and close the file when you are finished. Restart Apache to implement your password policy:
The directory you specified should now be password protected.
Configuring Access Control with .htaccess Files
If you wish to set up password protection using .htaccess files instead, you should begin by editing the main Apache configuration file to allow .htaccess files:
Find the <Directory> block for the /var/www directory that holds the document root. Turn on .htaccess processing by changing the AllowOverride directive within that block from “None” to “All”:
Save and close the file when you are finished.
Next, we need to add an .htaccess file to the directory we wish to restrict. In our demonstration, we’ll restrict the entire document root (the entire website) which is based at /var/www/html, but you can place this file in any directory you wish to restrict access to:
Within this file, specify that we wish to set up Basic authentication. For the AuthName, choose a realm name that will be displayed to the user when prompting for credentials. Use the AuthUserFile directive to point Apache to the password file we created. Finally, we will require a valid-user to access this resource, which means anyone who can verify their identity with a password will be allowed in:
Save and close the file. Restart the web server to password protect all content in or below the directory with the .htaccess file:
Confirm the Password Authentication
To confirm that your content is protected, try to access your restricted content in a web browser. You should be presented with a username and password prompt that looks like this:
If you enter the correct credentials, you will be allowed to access the content. If you enter the wrong credentials or hit “Cancel”, you will see the “Unauthorized” error page:
Conclusion
How To Decrypt Htpasswd Password Cmd
You should now have everything you need to set up basic authentication for your site. Keep in mind that password protection should be combined with SSL encryption so that your credentials are not sent to the server in plain text. To learn how to create a self-signed SSL certificate to use with Apache, follow this guide. To learn how to install a commercial certificate, follow this guide.
Latest versionReleased:
Library to work with htpasswd user (basic authorization) and group files.
Project description
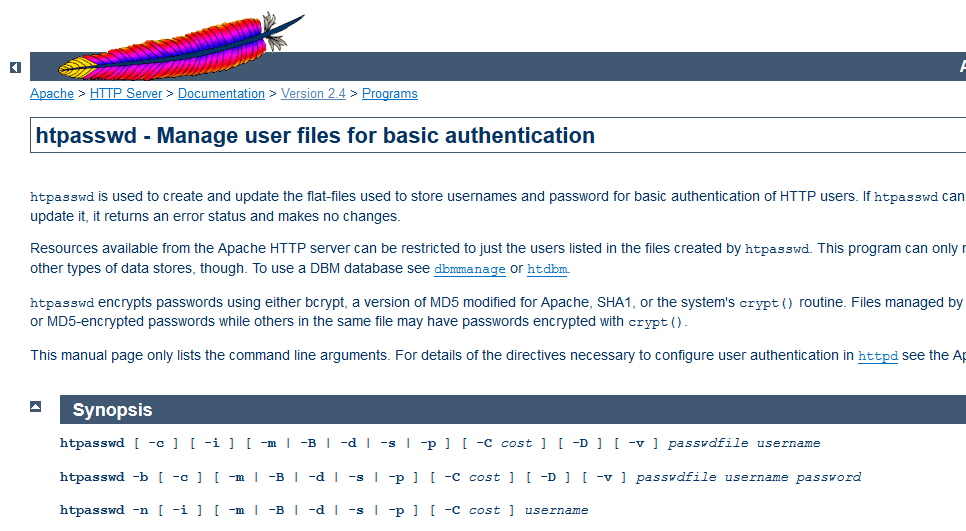
# htpasswd [](http://travis-ci.org/thesharp/htpasswd)
## Descriptionhtpasswd is a library for working with htpasswd user (only basic authorization) and group files. It supports CRYPT and MD5 encryption methods. To actually use MD5 encryption method you MUST have an openssl binary installed into system $PATH.
## Dependencies- Python 2.7 or 3.3 or 3.4- [orderedmultidict](http://pypi.python.org/pypi/orderedmultidict/0.7) >= 0.7- [future](https://pypi.python.org/pypi/future)- [nose](http://pypi.python.org/pypi/nose/) >= 1.1.2 (for tests)

import htpasswd
- with htpasswd.Basic(“/path/to/user.db”) as userdb:
- try:
- userdb.add(“bob”, “password”)
- except htpasswd.basic.UserExists, e:
- print e
- try:
- userdb.change_password(“alice”, “newpassword”)
- except htpasswd.basic.UserNotExists, e:
- print e
- with htpasswd.Group(“/path/to/group.db”) as groupdb:
- try:
- groupdb.add_user(“bob”, “admins”)
- except htpasswd.group.UserAlreadyInAGroup, e:
- print e
- try:
- groupdb.delete_user(“alice”, “managers”)
- except htpasswd.group.UserNotInAGroup, e:
- print e
To use MD5 encryotion, add mode='md5' to the constructor:
How To Decrypt Htpasswd Passwords
with htpasswd.Basic(“/path/to/user.db”, mode=”md5”) as userdb
## Provided methods
### Basic- __contains__(user)- users- add(user, password)- pop(user)- change_password(user, password)- _encrypt_password(password)
Decrypt A Password For Free
### Group- __contains__(group)- groups- is_user_in(user, group)- add_user(user, group)- delete_user(user, group)
## Exceptions
### UserExistsRaised by Basic.add if user already exists.
### UserNotExistsRaised by Basic.delete and Basic.change_password if there is no such user.
### GroupNotExistsRaised by Group.delete_user if there is no such group.
### UserAlreadyInAGroupRaised by Group.add_user if user is already in a group.
### UserNotInAGroupRaised by Group.delete_user if user isn’t in a group.
### UnknownEncryptionModeRaised by _encrypt_password if mode is not ‘crypt’ or ‘md5’.
Release historyRelease notifications | RSS feed
2.3
2.1
2.0
1.0
Download files
Download the file for your platform. If you're not sure which to choose, learn more about installing packages.
| Filename, size | File type | Python version | Upload date | Hashes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Filename, size htpasswd-2.3.tar.gz (3.8 kB) | File type Source | Python version None | Upload date | Hashes |
Htpasswd Decrypt Password
Hashes for htpasswd-2.3.tar.gz
How To View Encrypted Password
| Algorithm | Hash digest |
|---|---|
| SHA256 | 565f0b647a32549c663ccfddd1f501891daaf29242bbc6174bdd448120383e3d |
| MD5 | 73607c4b3443786dbc591616578c63ea |
| BLAKE2-256 | b92f8b76f8b77125b75c3532966f3291f9e8787268be65fc4c9694887cba9375 |
